Openssl provides command line tool to let user operate the security functions conveniently in terminal. This official site describes openssl command in details. As we know, openssl is an open source project so we can dig into the concrete internal code of a command. This page describes how to configure the openssl source code project in VSCode to debug openssl command.
Code structure
In this page, I take openssl 3.0.8 as example. Download the code from https://github.com/openssl/openssl . Let’s see the root folder below. Here we only focus on the crypto and apps folder.
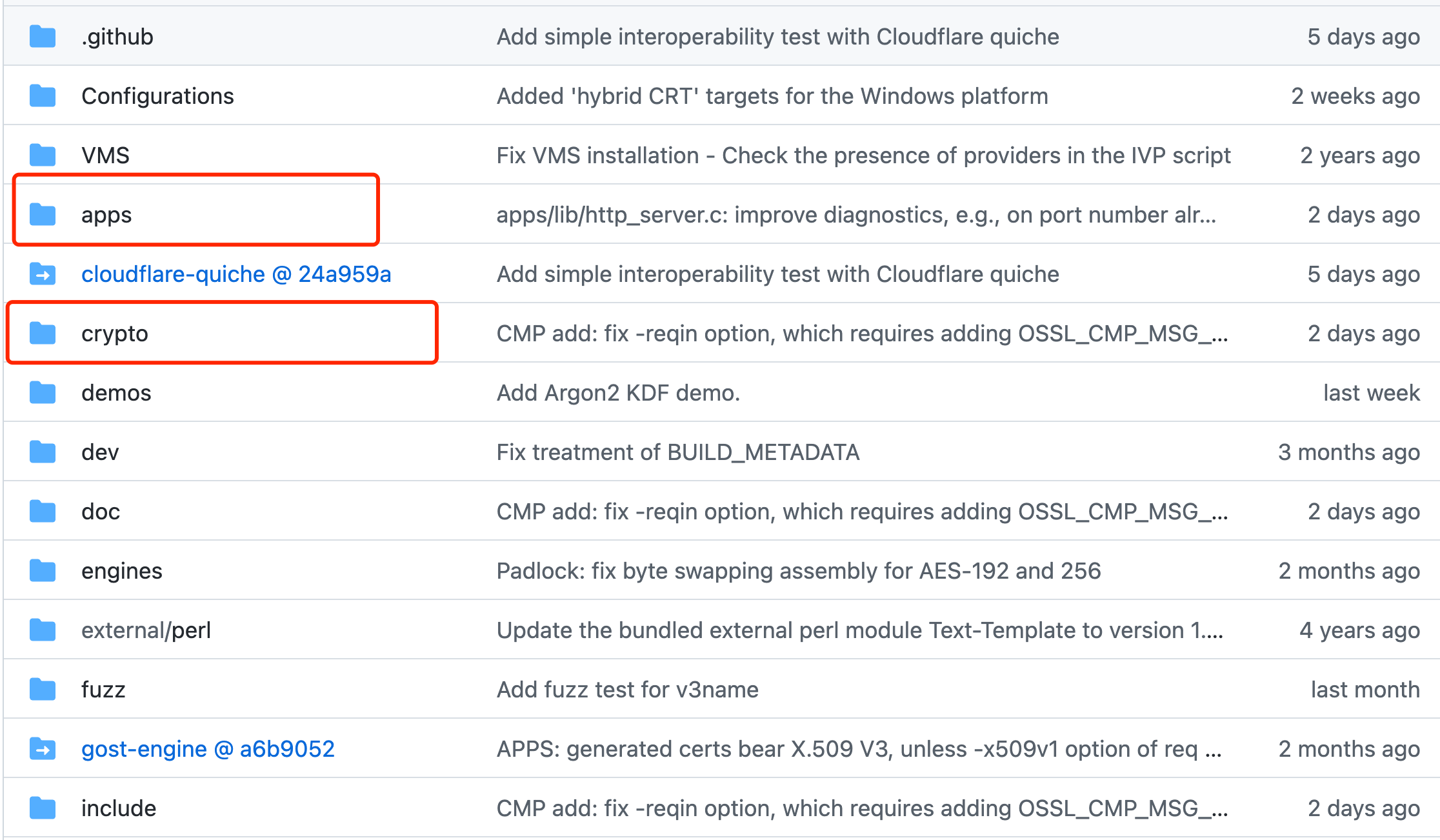
The crypto folder is the core of openssl. It contains the implementation of encrypted algorithm and other security features. The apps folder is just the command line entry point. We should first build crypto then let apps link to crypto whose library name is libcrypto.a.
How to build libcrypto.a
In the openssl root folder, run:
1 | ./config -d |
This is to make a debug configuration. “-d” means the ultimate library can be stepped into to see the code for debugger.
Then build, run:
1 | make clean |
“make clean” is to remove any intermediate generated files from previous build. If it is the first time, “make clean” can be neglected.
“make” is just to build the library.
After successful build, we can find the libcrypto.a in the root folder.
How to debug openssl command
Now we can debug openssl command. The whole thought is to directly run code in “apps” + libcrypto.a + header files.
We use VSCode IDE to set up the environment.
Here I don’t mention how to add C/C++ plugin/extension in VSCode and how to create tasks.json/launch.json template initially because these can be easily found on the Internet.
The file paths(/Users/weilin/…) mentioned afterwards are paths in my machine. You can easily replace them with your paths. The steps are:
-
Copy
appsfolder out to a new place and openappsin VSCode. -
Add
.vscode/tasks.jsonas below. This is just the completed gcc build command. Those code files after-gis just the C code to be built. (I used * wildcard in order not to type too many files here.)The “-I” part is additional header file search path. And we also specify thelibcrypto.a.
1 | { |
- Open
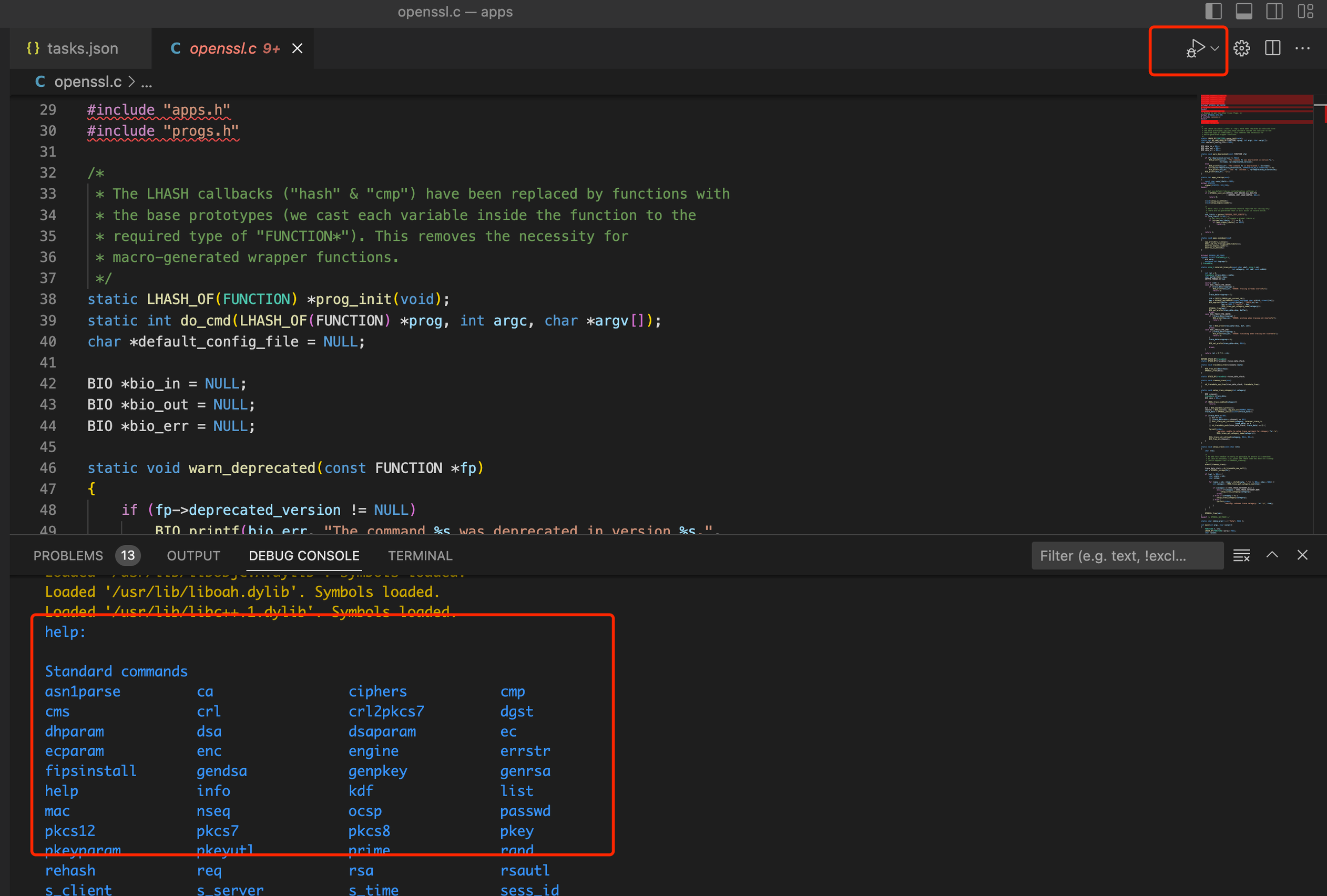
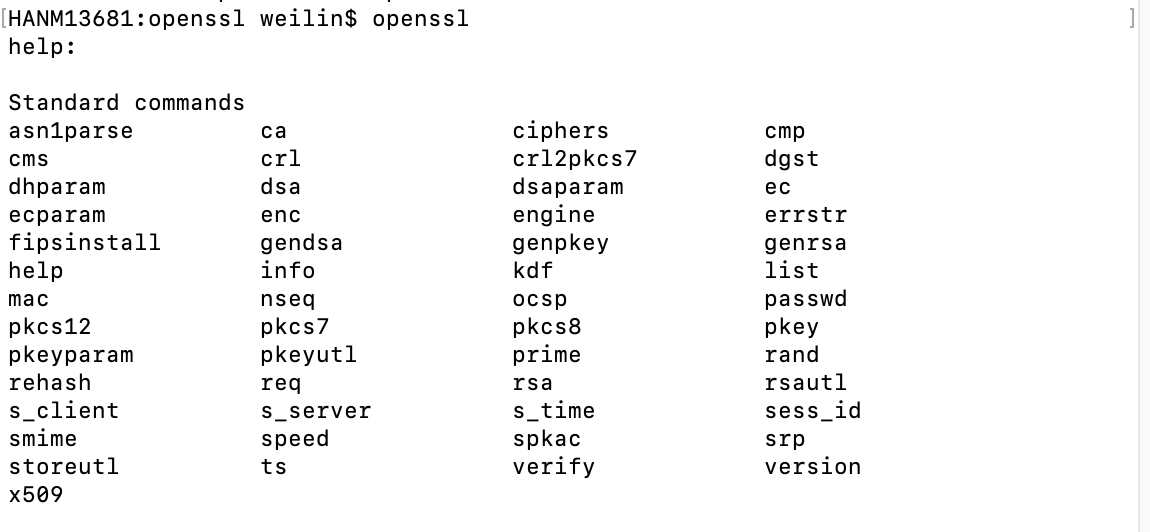
openssl.cfile. This is just the entry point of openssl command. You can find the beginning main function “int main(…)” in it. Tap the running button on top right, it will build and run the code. Because we don’t specify any command line arguments, the output is the help information. To confirm it, we can type “openssl” in terminal. The helper output are the same!
- Now we almost reach our goal. The only thing we should do is to specify the arguments. Suppose we need to debug this command:
1 | openssl pkcs12 -export -in cert_data -inkey myKey.pem -out mobileapp.p12 \ |
We should add the launch.json as below. The args part are just command line arguments.
1 | { |
Set the breakpoint. We can debug the code now! Have fun~